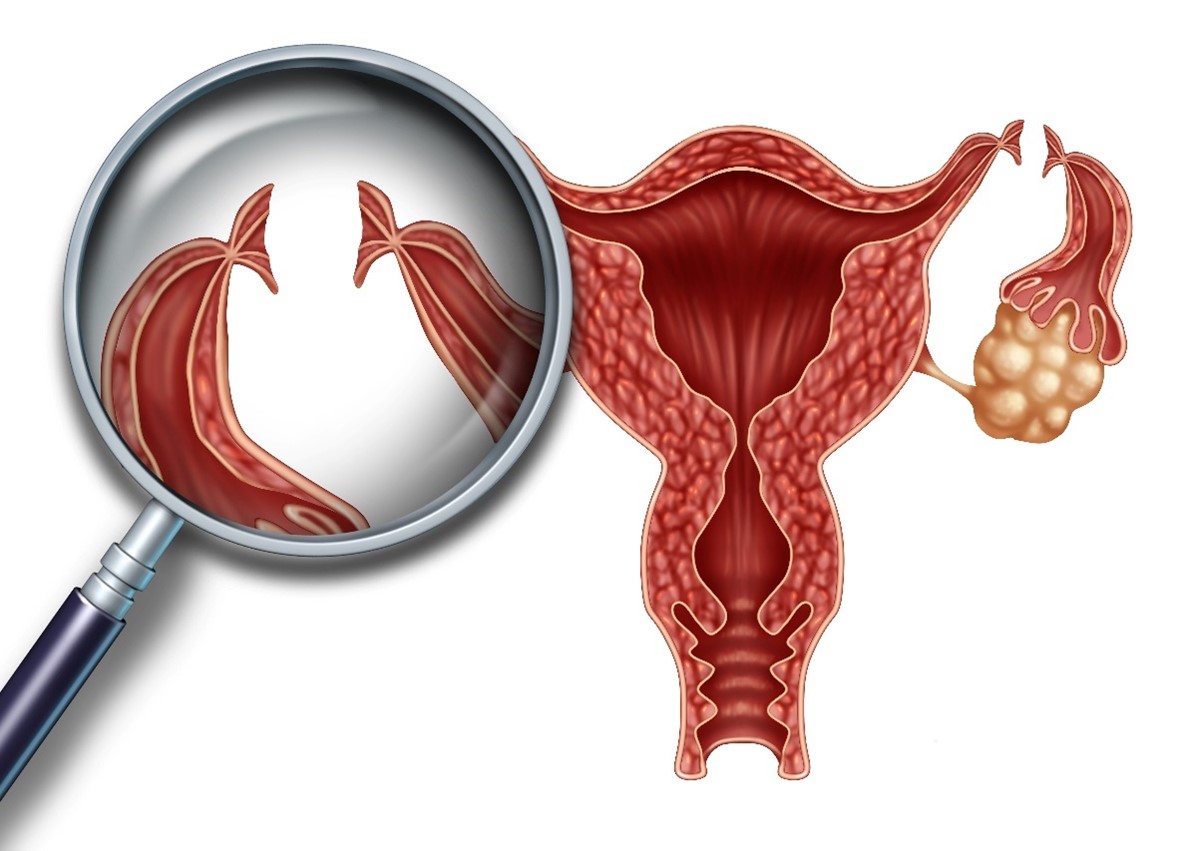
Laparoscopic bilateral tubal ligation is a permanent form of female sterilization commonly referred to as getting your “tubes tied.
” This technique requires only a few small incisions in the lower abdomen to access and seal both fallopian tubes, effectively preventing sperm from reaching the egg and thereby avoiding pregnancy.
This surgery is generally chosen by women who are sure they do not want to become pregnant in the future, as reversal is complex and often ineffective.
Reasons for Choosing the Surgery
This procedure is specifically for women who have decided against having more children.
The irreversible nature of tubal ligation makes it crucial to be sure of your decision, as reversal attempts are not performed and typically do not restore fertility effectively.
Surgical Procedure Details
The surgery begins with anaesthesia for comfort and involves the use of a laparoscope, a camera-equipped device inserted through a small navel incision to visualize the fallopian tubes.
Additional minor incisions are created to allow the use of surgical tools that either cut or seal the tubes.
The abdomen is inflated with air to improve access to the fallopian tubes.
Potential Risks and Preparations
Risks associated with this surgery include
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Damage to nearby organs
- The possibility of further surgeries
- Contraceptive failure
- Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy if conception occurs
Preparation involves:
- Fasting from midnight before the surgery
- Arranging transportation due to the effects of anaesthesia
- Arriving two hours before the scheduled time
It is also important to discuss medication adjustments with your doctor and schedule pre- and postoperative appointments.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
Post-surgery, expect soreness, and potential bruising around the navel and abdomen, shoulder, and back discomfort from the surgical gas.
You might also experience weakness and nausea from the anaesthesia.
Recovery instructions include:
- Not removing bandages for 24 hours, letting skin adhesives or stitches dissolve naturally
- Avoid soaking in bathtubs or swimming
- Showering is permitted, but be gentle around incision sites
- Managing activity levels, starting with rest and gradually increasing to light activities and short walks.
- Resuming sexual activity based on personal comfort
Follow all recovery guidelines closely to promote healing and monitor for complications.
Contact your doctor if you experience unusual symptoms or have concerns during recovery.