Pregnancy brings joy and anticipation, but it also requires careful attention to potential complications like pre-eclampsia. This condition, affecting about 5-8% of pregnancies globally, can arise in the latter half of gestation and demands vigilant monitoring and management for the health of both mother and baby.
What is Pre-eclampsia?
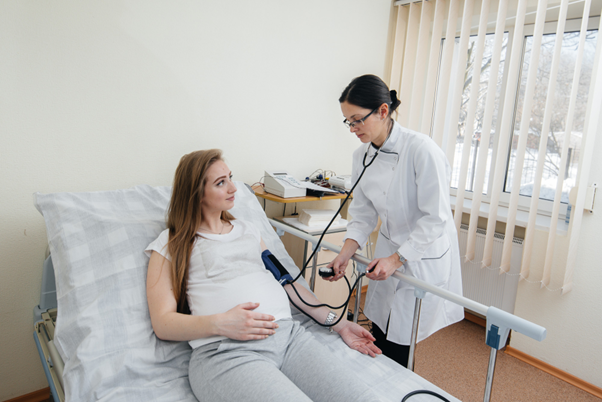
Pre-eclampsia is a pregnancy-related condition marked by high blood pressure (hypertension) and signs of organ damage, typically affecting the kidneys and liver. It typically emerges after 20 weeks of pregnancy and can vary from mild to severe. If left untreated, pre-eclampsia poses serious risks for both mother and baby.
Symptoms of Pre-eclampsia
Signs of pre-eclampsia may include:
- High blood pressure
- Swelling, particularly in the hands and face
- Rapid weight gain
- Presence of protein in the urine (proteinuria)
- Persistent and severe headaches
- Changes in vision, such as blurred vision or seeing spots
- Pain in the upper abdomen, usually on the right side
Not all women with pre-eclampsia experience symptoms, highlighting the importance of regular prenatal care and monitoring.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause remains unclear, several factors contribute to the development of pre-eclampsia:
- Placental issues affecting blood flow
- Genetic predisposition, with a family history of pre-eclampsia increasing risk
- First pregnancy or with a new partner
- Advanced maternal age or obesity
- Underlying medical conditions like chronic hypertension, diabetes, kidney disease, or autoimmune disorders
Managing and Treating Pre-eclampsia
Managing pre-eclampsia focuses on close monitoring and timely interventions to prevent complications:
- Regular prenatal check-ups to monitor blood pressure, urine for protein, and overall organ function
- Medications to control blood pressure and reduce risks
- Hospitalization for severe cases to monitor closely and possibly deliver the baby if conditions worsen
- Delivery of the baby, as it remains the definitive treatment for pre-eclampsia, depending on the severity and gestational age
Preventing Pre-eclampsia
While not entirely preventable, some measures can help reduce the risk:
- Regular prenatal care for early detection and management
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition and physical activity
- Consideration of low-dose aspirin therapy for high-risk individuals, as recommended by healthcare providers
Pre-eclampsia demands attention during pregnancy due to its potential impact on maternal and foetal health. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and risk factors empowers women and healthcare providers to identify and manage the condition promptly. With effective monitoring and treatment, the majority of women with pre-eclampsia can achieve positive outcomes for themselves and their babies. Regular prenatal care remains essential in detecting and managing pre-eclampsia to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy journey.